| Visual Basic (Declaration) | |
|---|---|
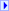
Public Property DefaultAuthenticationContext As IAuthenticationContext | |
| Visual Basic (Usage) |  Copy Code Copy Code |
|---|---|
Dim instance As Authenticator Dim value As IAuthenticationContext instance.DefaultAuthenticationContext = value value = instance.DefaultAuthenticationContext | |
| C# | |
|---|---|
public IAuthenticationContext DefaultAuthenticationContext {get; set;} | |
| C++/CLI | |
|---|---|
public: property IAuthenticationContext^ DefaultAuthenticationContext { IAuthenticationContext^ get(); void set ( IAuthenticationContext^ value); } | |
You may directly set the DefaultAuthenticationContext using the AuthenticationContext returned from a Login or LoginAsync call. Any EntityManager with a IdeaBlade.EntityModel.EntityManagerOptions.UseDefaultAuthenticationContext setting of true will then not need to be logged in separately, and will use the shared context set here. Using the DefaultAuthenticationContext provides single sign-on and single sign-off capabilities to your application.
The DefaultAuthenticationContext will also be set automatically by DevForce if EntityManager.Login or EntityManager.LoginAsync is called and that EntityManager has a IdeaBlade.EntityModel.EntityManagerOptions.UseDefaultAuthenticationContext setting of true.
Target Platforms: Windows 98, Windows NT 4.0, Windows Millennium Edition, Windows 2000, Windows XP Home Edition, Windows XP Professional, Windows Server 2003 family, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 family